Think of your mind as a huge information collection that grows every time you meet someone new. Each person adds details—like what they like, how they behave, and what they think. This steady stream of new information helps you understand better and make smarter decisions. Every interaction, every piece of consumer data captured, feeds into a larger system that enhances business acumen, mirroring our own cognitive processes. The business world, similar to shared human memory, is using this vast amount of data not just as a tool but as a key part of how it operates and makes decisions.
The growth of the big data and business analytics market, from $198.08 billion in 2020 to an expected $684.12 billion by 2030 (Statista), highlights this significant evolution. It illustrates a shift in how businesses absorb, process, and utilize information to navigate and lead in a complex, interconnected economy.
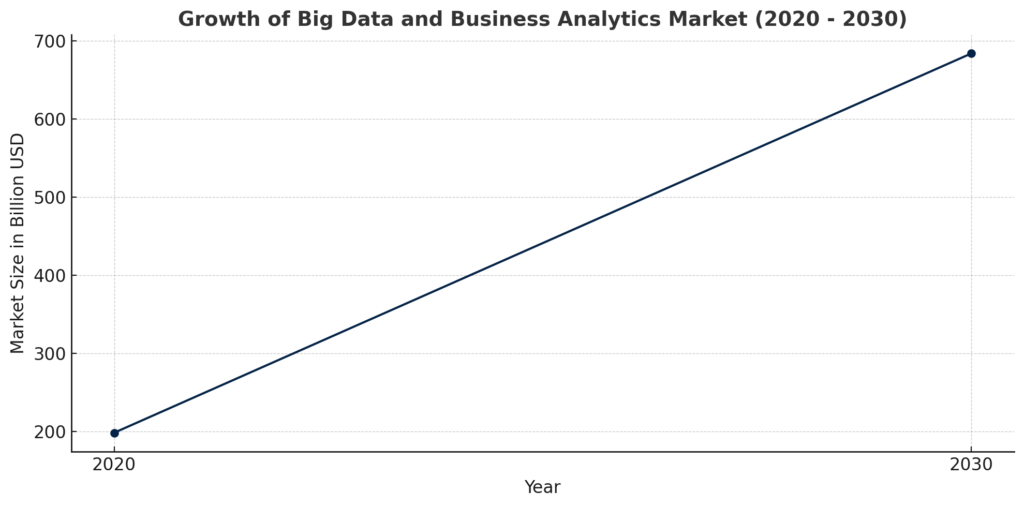
Table of Contents
Evolution and Importance: Learning from Data
As humans evolve from basic knowledge to complex understanding, so has big data analytics. What started as simple data collection has transformed into a sophisticated predictive and prescriptive powerhouse, enabling businesses to anticipate trends and act decisively. This maturity mirrors human development, from recognizing simple patterns to solving complex problems.
Core Components: The Pillars of Big Data
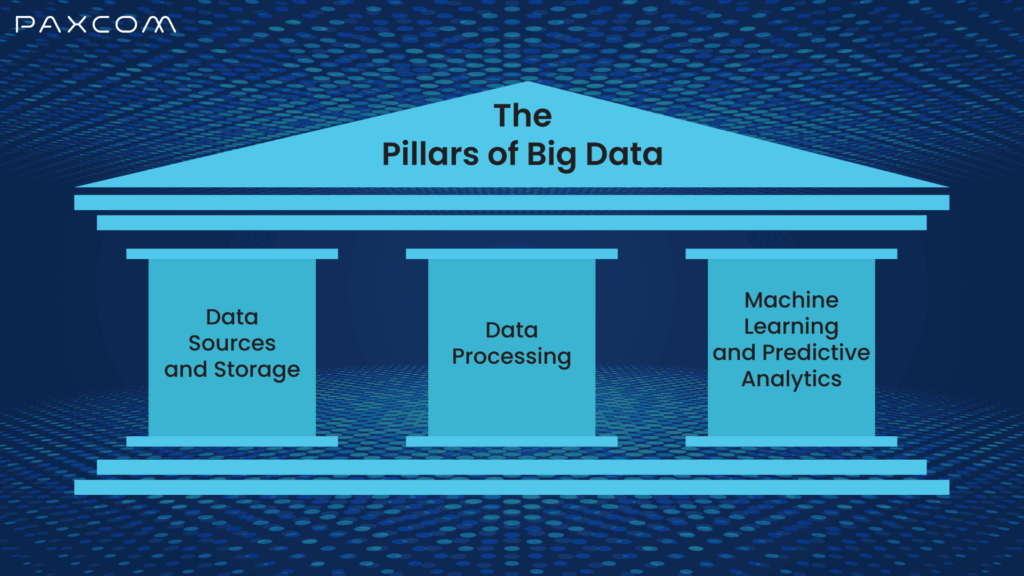
Understanding the core components of big data is essential for leveraging its full potential in business operations.
- Data Sources and Storage: Businesses need robust and secure storage solutions to manage diverse data sources. These solutions ensure that data is protected and easily accessible.
- Data Processing: Transforming raw data into actionable insights ensures businesses aren’t just data-rich but also insight-savvy.
- Machine Learning and Predictive Analytics: These technologies enable businesses to forecast trends and behaviors accurately. By analyzing past data, machine learning and predictive analytics help make precise predictions and informed strategic decisions.
Big Data Analytics Trends in 2024
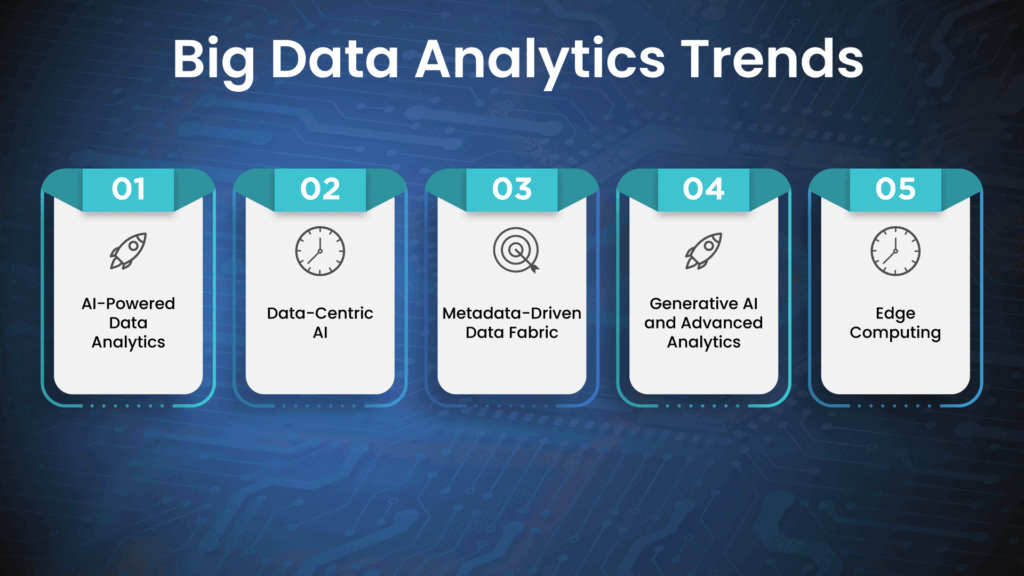
- AI-Powered Data Analytics: This trend significantly enhances our analytical capabilities and improves decision-making processes. By leveraging AI, we can understand data deeper and extract meaningful insights.
- Data-Centric AI: This approach prioritizes data as the foundation of all decisions, ensuring that data quality and relevance are prioritized.
- Metadata-Driven Data Fabric: Combining the simplicity and consistency of a data fabric with the intelligence and automation capabilities of metadata, this powerful method enables us to manage and utilize data more effectively, leading to faster and more informed decisions.
- Edge Computing: By bringing computation and data storage closer to where it’s needed, edge computing reduces the need for long-distance data transmission, enabling real-time processing and analysis. In AI, deploying models directly on edge devices allows faster processing, lower latency, and improved security.
- Generative AI and Advanced Analytics: Generative models can create synthetic data, while advanced analytics offer predictive and prescriptive capabilities. Together, they provide organizations with deeper insights, more informed decision-making, and the ability to drive innovation across various domains such as healthcare, finance, and marketing.
Industry Applications: Big Data at Work
- Finance- Streamlining Assessments, Deepening Analysis
Financial institutions leverage big data analytics to streamline assessment processes and deepen their analysis of market conditions, customer behavior, and transaction patterns. This enables more informed decision-making, risk mitigation, and optimized investment strategies, similar to how continuous learning about investment strategies and market trends can improve personal financial literacy.
- E-commerce- Understanding Consumer Behavior, Tailoring Advice
Picture a scenario where you have a close friend who shares their preferences with you. You can tailor your advice and recommendations to their unique needs and interests. E-commerce companies are doing something similar by analyzing consumer behavior through data analytics. By understanding customer preferences, browsing history, and purchase patterns, they can personalize product recommendations, optimize marketing strategies, and enhance the overall customer experience.
- Manufacturing- Enhancing Efficiencies, Optimizing Routines
Manufacturing companies are leveraging big data analytics to enhance their operational efficiencies. By monitoring equipment performance, detecting anomalies, and predicting maintenance needs, they can minimize downtime, optimize production processes, and ensure product quality.
- Logistics- Managing Inventory, Planning Efficient Routes
Consider how you rely on past experiences and navigation apps to determine the most efficient routes, considering traffic, construction, and weather conditions. Logistics companies do something similar by managing their inventory and supply chains efficiently. By analyzing data from sales forecasts, supplier performance, and transportation networks, they optimize inventory levels, reduce costs, and ensure the timely delivery of goods.
The Benefits: Why Invest in Big Data Analytics?
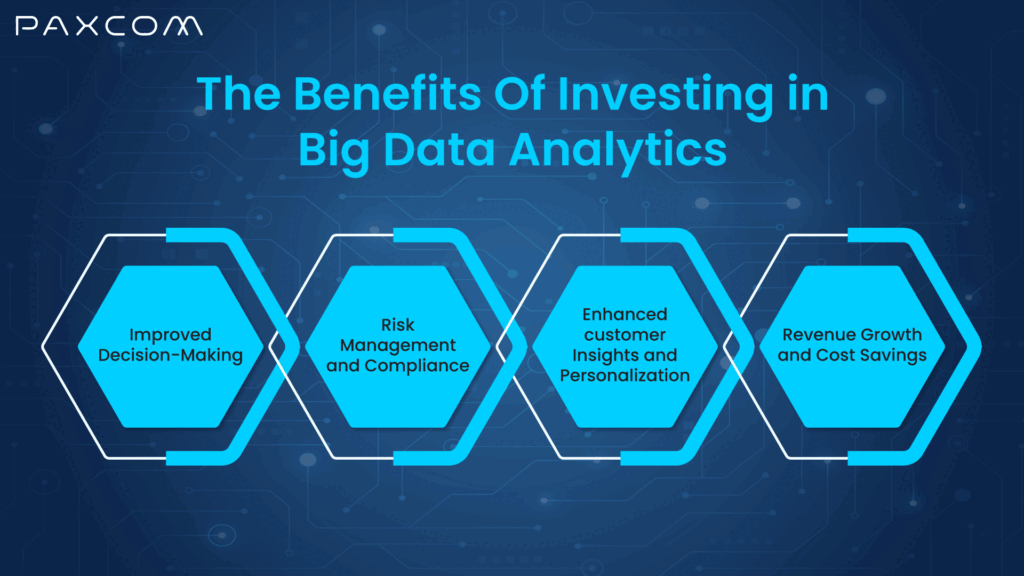
Investing in big data analytics offers a suite of benefits that can fundamentally alter how a business operates:
- Improved Decision-Making: Gone are the days of relying on gut feelings. Big data analytics lets you make decisions based on solid evidence. You can spot trends and patterns by analyzing large datasets, leading to more accurate forecasts and strategic plans.
- Enhanced customer insights and personalization: Analyzing customer preferences and behaviors allows businesses to personalize products and services, boosting customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Risk Management and Compliance: Imagine having a radar that spots risks before they hit. That’s what analytics can do. This proactive approach helps businesses avoid potential disruptions, protect assets, and strengthen their reputation.
- Revenue Growth and Cost Savings: It enhances marketing strategies, optimizes pricing, and improves sales tactics. With advanced insights, you can target the most profitable customers and maximize returns through upselling and cross-selling.
Challenges and Solutions of Big Data Analytics
Despite the clear benefits, the road to big data mastery isn’t without its bumps:
- Data Volume and Integration: Scalable cloud solutions and robust ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) tools are essential to effectively managing the surge of data from diverse sources.
- Data Quality: Rigorous data governance is crucial to ensure data accuracy and readiness for analytics.
- Skill Shortages: Upskilling and strategic hiring are key to filling the data expertise gap.
- Data Security: Implementing robust security protocols is mandatory to protect sensitive data against escalating cyber threats.
Choosing the Right Big Data Analytics Services Provider: Key Consideration
- Understand Your Industry Needs
The first step is recognizing that not all big data solutions are equal. For instance, a CPG company might require an analytics provider that excels in supply chain optimizations and consumer trend forecasting, while a financial firm might need robust risk assessment capabilities.
- Scalability and Flexibility
Choose a provider whose tools grow with your business. Whether expanding product lines in retail or diversifying assets in finance, your analytics services should seamlessly scale up to handle increased data volumes and complexity without compromising performance.
- Integration Capabilities
Your provider should offer solutions that integrate effortlessly with your existing IT infrastructure. This integration minimizes disruption and leverages your current data systems, enhancing overall efficiency and data coherence.
- Compliance and Security
Particularly crucial in finance, compliance with regulatory standards and robust data security protocols are non-negotiable. Ensure your provider meets the industry-specific compliance requirements and offers advanced security measures to protect sensitive information.
- Proven Track Record
Look for providers with established credibility and a portfolio of successful implementations across your industry. Case studies and testimonials can provide insights into their capabilities and the effectiveness of their solutions in real-world scenarios.
Implementing Big Data Analytics in Your Organization
- Establish Clear Objectives:
Begin with the end in mind. What specific goals do you aim to achieve with big data analytics? Clear objectives will guide your analytics implementation, whether improving product placement and inventory management in retail, enhancing customer segmentation in CPG, or managing financial credit risks.
- Team up with the right people
Big data projects require various skills, including data scientists, IT specialists, and industry experts. Ensure your team understands big data technology and possesses deep industry knowledge to make the data actionable.
- Start with a Pilot Project
Before a full-scale rollout, start with a pilot project that addresses a specific area of need. This approach allows you to measure the impact of analytics, make necessary adjustments, and build a case for wider adoption within the organization.
- Leverage Data Governance
Data quality is paramount. Implementing robust data governance practices ensures the accuracy, completeness, and reliability of the data used in your analytics initiatives.
- Drive Adoption through Training and Support
Analytics must be embraced across the organization to be effective. Invest in training sessions that help employees understand and utilize the analytics tools provided. Ongoing support and resources can help ease new technology resistance.
- Review and Iterate:
Finally, analytics is an ongoing process. Review the outcomes of your analytics efforts regularly against your set objectives. This feedback loop is crucial for continuous improvement and helps refine strategies to maximize the return on your analytics investment.
Examples of successful big data implementations in business
1. Retail: Personalized Customer Experiences at Walmart

Walmart, one of the largest retailers globally, has effectively harnessed big data to personalize customer experiences and improve sales. By analyzing massive amounts of consumer data, Walmart offers personalized product recommendations and optimizes its stock levels based on real-time buying trends. This strategy not only enhances customer satisfaction but also increases operational efficiency. By harnessing the power of big data, Walmart has seen impressive results, including a 10-15% increase in online sales, a 40% increase in ecommerce sales, and the strongest U.S. sales growth in over a decade, as per CFO Dive.
2. Finance: Risk Management at American Express
American Express uses big data to enhance fraud detection and credit risk analysis. By analyzing transaction data in real-time, AmEx can identify unusual patterns and potential fraud, significantly reducing financial losses. Additionally, their predictive analytics tools help forecast customer loyalty and future spending patterns, tailoring offers to individual consumer preferences. American Express has developed tools like Enhanced Authorization (EA), which allows merchants and AmEx to identify who is behind a credit card transaction by analyzing additional information such as IP address, email address, and shipping address. This has reduced fraudulent transactions by 60% and is offered free of charge to merchants, as per Harvard Digital Initiative.
3. Consumer Packaged Goods (CPG): Supply Chain Efficiency at Procter & Gamble (P&G)
Procter & Gamble utilizes big data to optimize supply chain operations and predict market trends. Their sophisticated analytics tools help forecast demand more accurately, manage inventories efficiently, and reduce operational costs. This proactive approach enables P&G to maintain its leadership in the competitive CPG industry.
4. Healthcare: Improving Patient Outcomes with Predictive Analytics
Major healthcare providers are adopting big data to improve patient outcomes and reduce costs. For example, predictive analytics are used to customize patient treatments and anticipate health deteriorations before they become critical. This improves the quality of care and significantly decreases healthcare costs by reducing hospital readmissions.
These examples demonstrate how big data can be applied in various industries to solve specific problems, enhance efficiency, and create more personalized user experiences. Each case highlights the importance of a clear strategy and the right tools to effectively harness big data’s power.
Conclusion
As we advance into 2024 and beyond, big data analytics remains not just a tool but a strategic pillar essential for any forward-thinking business. The challenges are surmountable with the right approach and technology, and the benefits are substantial. Embrace big data analytics, and you’re not just participating in the future; you’re actively shaping it. Data isn’t just valuable in the race for innovation and efficiency—it’s the foundation.














